The Ultimate Gear Oil Guide
There is a stark difference between gear oil and engine oil. As many commonly believe, they are not interchangeable. They both have varying properties and functions. In simple terms, engine oils cater to vehicle engines. Whereas gear oils are used in gear systems. They more specifically apply to transmissions, transfer cases, and differentials in automobiles, trucks, and other machinery. This ultimate gear oil guide will solve most of your questions related to gear oil.
What is Gear Oil?
Gear oils are fluid lubricants that are used for transmissions, manual gearboxes, differentials, transaxles and transfer cases in your car or truck. It has a highly viscous fluid and often includes organosulfur compounds. These are lubricating oils that protect the transmission and gearbox internal parts from wear and tear.
What Additives are used in Gear Oils?
Various additives are added to the lubricants to enhance the performance of the base oil. For better resistance of the hypoid bevel gears, most gear oils are mixed with many additives such as;
- Extreme Pressure additives (EP)
- Anti-wear additives
- Oxidation inhibitors
- Rust and corrosion inhibitors
- Anti foaming agents
- Pour-point depressants
- Dithiocarbamate derivatives
- Sulfur-treated organic compounds
Gear oils fulfil more than one purpose. Given the wide range of functions, materials and conditions of a gearbox, these oils are critical in providing the necessary lubrication it needs.

What is the Use of Gear Oil?
The gear system of your car includes a gearbox, propeller shafts, hypoid bevel gears, transmissions, live axle, bearings etc. There are a lot of sliding actions and metal-to-metal contact. Gradually, this leads to excessive heat, internal part damage as well as corrosion. If not properly lubricated, the following problems will occur to the gear system;
- Corrosion
- Scuffing
- Wear Damage
- Pitting of vital drivetrain components
This will eventually lead to severe damage to the car’s transmission and gear systems of your car. Moreover, it will also hamper your car’s performance and the repair cost will be shattering. This is why regular use of gear oils is a vital component for your car maintenance.
The main function of gear oils is to lubricate transmission, differentials and transfer cases. It protects the crucial internal parts of the gear system against all of the damages above. Additionally, gear oil lubrication helps the system perform smoothly and gives a cooling effect.

How does Gear Oil Work?
Gear oils have high viscosity. The thickness in the fluids provides easy distribution and ample protection to the gear set. In contrast, engine oils work in a setting where they come in contact with pollutants, acids and gases, which are by-products of combustion. However, gear oils do not come in contact with any of that. Under the rigorous environment of the gear system set, these fluid lubricants do a better job at protecting the vital hardware within the axles. Overall, they make the gears slide easily and help get efficient performance out of your vehicle.
What are the Qualities of Gear Oil?
There is more to gear oils than smooth lubrication and prohibiting heat, wear damage. There are other properties that make it an effective lubricant for automotive as well as industrial setting.
- Adhesive – The ability to stick to the metal surface of the gears helps prevent wear from direct metal contact
- Inhibition of Foam – Due to the rigid motion of gears there is a possibility of foam formation. Anti-foaming agents in the oils combat this and keep the parts running hassle-free.
- Formation of Low Emulsion – More helpful in industrial purposes, this quality can tackle corrosion and oxidation of the oil.
- Minimum Contact with Components – There are certain gearbox elements that may interact with the oils. To avoid this, gear oils with the right additives will restrict interaction.
When Should we Change Gear Oil?
Even though it is vital to regularly change the gear oil you use, there isn’t a specific timeline as to when you change it. Your car manual should have the relevant information so it is helpful to check it out. However, it is recommended that you change your gear oil for the following conditions.
For automatic gear transmission: Up to 80,000 km (50,000 miles)
For manual gear transmission: Up to 1,60,000 km (100,000 miles)
What are the Types of Gear Oil?
Depending on various conditions and functions, there are different gear oils with varying additives. At operating temperatures, these lubricants perform specific applications. Gear oils can be classified into the following types;
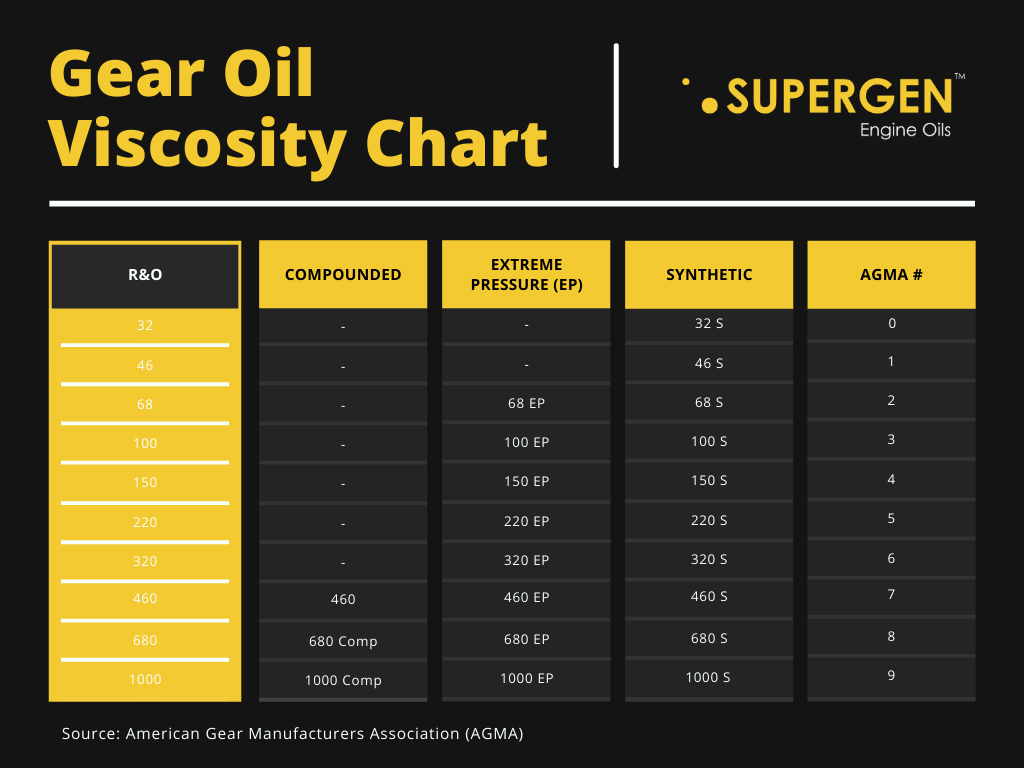
R & O (Rust and Oxidation) Gear Oils
This type of gear lubricant is specifically designed for corrosion reduction in the gearbox. They also operate in regards to chemical stability, suppressing foam and demulsibility. Many gear oils have corrosion-reducing qualities.
They perform well at high speeds, uniform loading and low loads. One of the significant benefits of these oils is that it extends the life of the oil. It does not include additives of anti-scuff or lubrication. These oils are classified in ISO (International Standards Organisation Viscosity Grade) grades of 32-320EP (Extreme Pressure) Gear Oils
Also known as anti-scuff lubricants, these have more superior characteristics than R & O gear oils. Their main objective is to endure heat and pressure under extremely harsh conditions. To achieve this, many special additives such as sulfur phosphorus are in use.
The drawback of this oil is it’s potential to corrode metal surfaces. Hence, it is advised for you to be careful while using this oil for the appropriate machine.
Compounded Gear Oils
To have better lubricity and film strength, some gear oils are mixed with fat (synthetic fatty acids). Commonly used in worm gear applications. These oils are suitable for high-pressure applications, low speeds and maintaining good quality lubrication. This is accomplished when mixed with the right additives.
Synthetic Gear Oils
As opposed to synthetic engine oils which are more superior in quality and more preferable than its counterparts, synthetic gear oils have a more specific function. They are used in rigorous machine conditions, in super high/low temperatures and high pressures. They will perform well in circumstances other oils are not fit for.
Viscosity in Gear Oils
Viscosity is the resistance of a fluid to flow. It depends upon the thickness of the fluids. The thinner the lubricant, the more easily it will flow.
When it comes to gear oils, highly viscous (high viscosity) oils are better for low speeds with rough surface loaded gears. A thick gear lubricant will perform better protection to wear and damage to internal gear parts.
It is difficult to find out which exact viscosity gear oil is best for your car but your car manual will certainly be of help. Moreover, there are various common standards for determining viscosity. Most commonly referred to are as follows;
- American National Standards Institute (ANSI)
- American Gear Manufacturer Association (AGMA)
Why is Thermal Stability important?
Gear systems have various parts that are constantly in motion. This increases the level of heat in the gears. Furthermore, heat builds up slowly in more active and agile gears and faster in slower ones.
But, the load is higher in slower gears and hence, there is an increase in pressure. To combat all of this, stable gear oil is extremely necessary.
If an oil is not stable, it will deteriorate sooner and make more impurities which hamper the performance and life of the gear oil in a short amount of time. Therefore, it is vital to choose a gear oil keeping in mind the gear system it will be used for.
How to Choose Gear Oil?
Many advise that you refer to your vehicle’s manual while making a decision. It mentions all the gear set specifications and the gear oil recommendation. If you do not follow the manual’s instructions and use some other gear oil than advised, your car will underperform and possibly lead to damage to sensitive gear parts. It is also important to note that gear specifications change from car to car.
Many gear oils in the market are known as ‘universal gear oils’. They apply to manual transmissions. Presently, recycled-used gear oils are used very commonly. These oils can be reused after removing the chemical and physical impurities being collected over time.
Gear oils deteriorate over time. The friction from the gear system grinding leads to tiny metal particles accumulating in the oil. This eventually inhibits the gear oil from performing effectively.
When you use the Original Equipment Manufacturer, OEM-recommended product or a similar quality product, you’re bound to have no issues. But if cut costs and settle for a lower-quality product, the change in performance will be quite noticeable.
It is important to upkeep your gear system with standardized and superior products to get the best out of your car. Many premium gear oils consist of anti-wear additives which make the product more durable. Furthermore, using gear oils with dispersants additives lead to sludge reduction as well as the built-up varnish of carbon.
What is Base Oil Selection?
Before we select a gear oil, we must first base oil selection. Any lubricant consists of base oils. For example; mineral engine oils have the base oil of petroleum crude oil.
Mineral gear oils are more preferable in most cases due to their high pressure-coefficient and thicker film strength. On the other hand, synthetic gear oils have higher oxidation resistance and have better thermal stability.
Hence, they are more used in conditions with high operating temperatures. In situations with low ambient temperatures, synthetic oils are more apt for use.
Which Gear Oil is Best for Your Car
Choosing the right and ideal gear oil for your car depends on the following factors;
Type of Gearbox
It’s essential to take into consideration the dimensions of the gearbox, the sliding features, the metals, gear ratio, etc.
Impacts of gear oil on the gear system during leaks
Certain characteristics of lubricants such as anti-corrosive and extreme pressure oils if not used proper consideration and usage can result in more harm than good. Biodegradable oils that do not stain are also preferred in the event of a leakage.Temperature of Service Oil
Temperatures affect lubricants and it’s viscosity. This can result in a change in its thickness. Gear oils at normal temperatures should be between 90 to 100 ℉ (50 to 55 ℃).Influence of the gear system on the Oil
If exposed to humidity or dust, gear oils have enhanced properties to extend the life of its performance.Operating Conditions
It’s important to acknowledge the loads, the vibrations and shock levels, high pressures and anti-wear properties before making a decision.Maintenance and Upkeep
Using synthetic oils will cut down your costs as it requires fewer oil changes.
What is Gear Oil Grading?
The base grade determines the gear oil standard. It defines most of its specifications. The American Petroleum Institute has put out a few gear oil standards, most commonly used in modern cars.
Most of them are no longer in production and only a few remain. It was in the range of “Lubricant Service Designations for Automotive Manual Transmissions, Manual Transaxles, and Axles”.
API GL-1
These are fundamentally applied for low-use manual transmissions. The operating conditions consist of low pressures and have a minimum number of additives. Anti-corrosive and extreme pressure additives are not found in this type of oil.
API GL-2
Primarily used for worm-gear types of axles, these have more additives than what is present in GL-1. Extreme pressure additives are absent in these.
API GL-3
These oils are a good middle-ground for oils that perform better than GL-1 and GL-2. Although, they fall behind GL-4 in terms of performance. They are generally used for manual transmissions with moderate to somewhat extreme conditions. They also handle low pressure.
API GL-4
These are most generally used in this world. They specifically apply to passenger cars and light truck manual gear systems. Many transmissions work well with the use of this lubricant because it contains high-pressure additives at moderate levels. Its applications include tractor gearboxes and spiral bevel gear final drives.
API GL-5
These oils can withstand severely high pressures due to EP( extreme pressure) additives. It is classified for passenger cars, light and heavy trucks, and bus hypoid final drives where highly loaded systems and hypoid gears.
API MT-1
This type is newly included in gear oils for manual transmission in buses and heavy-duty trucks.
Conclusion
Gear oils and their applications could be tricky to understand. However, it is important to understand the basics for our convenience. Knowing their usages and benefits will help you tremendously when it comes to selecting the right one and when to change them. This will inevitably aid in getting the best out of your car. Hope this ultimate gear oil guide is useful for you.



